Pierre Raymond de Montmort: Difference between revisions
en>ZéroBot m r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding pt:Pierre Rémond de Montmort |
en>Waacstats →External links: Add persondata short description using AWB |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{continuum mechanics|cTopic=[[Solid mechanics]]}} | |||
A '''neo-Hookean solid'''<ref name=Ogden>Ogden, R. W. , 1998, '''Nonlinear Elastic Deformations''', Dover.</ref><ref name=Macosko>C. W. Macosko, 1994, '''Rheology: principles, measurement and applications''', VCH Publishers, ISBN 1-56081-579-5.</ref> is a [[hyperelastic material]] model, similar to [[Hooke's law]], that can be used for predicting the nonlinear stress-strain behavior of materials undergoing large [[Deformation (engineering)|deformation]]s. The model was proposed by [[Ronald Rivlin]] in 1948. In contrast to [[linear elasticity|linear elastic]] materials, the [[stress-strain curve]] of a neo-Hookean material is not [[linear]]. Instead, the relationship between applied stress and strain is initially linear, but at a certain point the stress-strain curve will plateau. The neo-Hookean model does not account for the [[dissipation|dissipative]] release of energy as heat while straining the material and perfect elasticity is assumed at all stages of deformation. | |||
The neo-Hookean model is based on the statistical thermodynamics of cross-linked polymer chains and is usable for [[plastic]]s and [[rubber]]-like substances. Cross-linked polymers will act in a neo-Hookean manner because initially the polymer chains can move relative to each other when a stress is applied. However, at a certain point the polymer chains will be stretched to the maximum point that the covalent cross links will allow, and this will cause a dramatic increase in the elastic modulus of the material. The neo-Hookean material model does not predict that increase in modulus at large strains and is typically accurate only for strains less than 20%.<ref name=Gent>Gent, A. N., ed., 2001, '''Engineering with rubber''', Carl Hanser Verlag, Munich.</ref> The model is also inadequate for biaxial states of stress and has been superseded by the [[Mooney-Rivlin solid|Mooney-Rivlin]] model. | |||
The [[strain energy density function]] for an [[incompressible]] neo-Hookean material is | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_{1} (I_1-3) \, | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>C_{1}</math> is a material constant, and <math>I_1</math> is the first [[Invariants of tensors|invariant]] of the [[finite strain theory|left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor]], i.e., | |||
:<math> | |||
I_1 = \lambda_1^2 + \lambda_2^2 + \lambda_3^2~ | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\lambda_i</math> are the [[finite strain theory|principal stretch]]es. | |||
For three-dimensional problems the [[compressible]] neo-Hookean material the strain energy density function is given by | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_{1}~(\bar{I}_1 - 3) + D_1~(J-1)^2 ~;~~ J = \det(\boldsymbol{F}) = \lambda_1\lambda_2\lambda_3 | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>D_1</math> is a material constant, <math>\bar{I}_1 = J^{-2/3} I_1</math> is the first invariant of the [[deviatoric]] part of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor, and <math>\boldsymbol{F}</math> is the [[deformation gradient]]. It can be shown that in 2D, the strain energy density function now becomes | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_{1}~(\bar{I}_1 - 2) + D_1~(J-1)^2 ~; | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\bar{I}_1 = I_1/J</math>. | |||
Several alternative formulations exist for compressible neo-Hookean materials, for example <ref name=Ogden/> | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_{1}~(\bar{I}_1 - 3 - 2\ln J) + D_1~(J-1)^2 | |||
</math> | |||
For consistency with linear elasticity, | |||
:<math> | |||
C_{1} = \cfrac{\mu}{2} ~;~~ D_1 = \cfrac{\kappa}{2} | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\mu</math> is the [[shear modulus]] and <math>\kappa</math> is the [[bulk modulus]]. | |||
== Cauchy stress in terms of deformation tensors == | |||
=== Compressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
For a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material the Cauchy stress is given by | |||
:<math> | |||
J~\boldsymbol{\sigma} = -p~\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2C_1~\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}}) | |||
= -p~\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + \frac{2C_1}{J^{2/3}}~\mathrm{dev}(\boldsymbol{B}) | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\boldsymbol{B}</math> is the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor, and | |||
:<math> | |||
p := -2D_1~J(J-1) ~;~~ | |||
\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}}) = \bar{\boldsymbol{B}} - \tfrac{1}{3}\bar{I}_1\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} ~;~~ | |||
\bar{\boldsymbol{B}} = J^{-2/3}\boldsymbol{B} ~. | |||
</math> | |||
For infinitesimal strains (<math>\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}</math>) | |||
:<math> | |||
J \approx 1 + \mathrm{tr}(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}) ~;~~ \boldsymbol{B} \approx \boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2\boldsymbol{\varepsilon} | |||
</math> | |||
and the Cauchy stress can be expressed as | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} \approx 4C_1\left(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon} - \tfrac{1}{3}\mathrm{tr}(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon})\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}}\right) + 2D_1\mathrm{tr}(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon})\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
Comparison with [[Hooke's law]] shows that <math>\mu = 2C_1</math> and <math>\kappa = 2D_1</math>. | |||
:{| class="toccolours collapsible collapsed" width="80%" style="text-align:left" | |||
!Proof: | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
The [[stress (physics)|Cauchy stress]] in a [[compressible]] hyperelastic material is given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = \cfrac{2}{J}\left[\cfrac{1}{J^{2/3}}\left(\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_1} + \bar{I}_1~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_2}\right)\boldsymbol{B} - | |||
\cfrac{1}{J^{4/3}}~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_2}~\boldsymbol{B} \cdot\boldsymbol{B} \right] + \left[\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial J} - | |||
\cfrac{2}{3J}\left(\bar{I}_1~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_1} + 2~\bar{I}_2~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_2}\right)\right]~\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
For a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material, | |||
:<math> | |||
\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_1} = C_1 ~;~~ \cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_2} = 0 ~;~~ \cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial J} = 2D_1(J-1) | |||
</math> | |||
while, for a compressible Ogden neo-Hookean material, | |||
:<math> | |||
\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_1} = C_1 ~;~~ \cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \bar{I}_2} = 0 ~;~~ \cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial J} = 2D_1(J-1) - \cfrac{2C_1}{J} | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, the Cauchy stress in a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material is given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = \cfrac{2}{J}\left[\cfrac{1}{J^{2/3}}~C_1~\boldsymbol{B} \right] + \left[2D_1(J-1)- | |||
\cfrac{2}{3J}~C_1\bar{I}_1\right]\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
while that for the corresponding Ogden material is | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = \cfrac{2}{J}\left[\cfrac{1}{J^{2/3}}~C_1~\boldsymbol{B} \right] + \left[2D_1(J-1)-\cfrac{2C_1}{J} - | |||
\cfrac{2}{3J}~C_1\bar{I}_1\right]\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
If the [[isochoric]] part of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor is defined as <math>\bar{\boldsymbol{B}} = J^{-2/3}\boldsymbol{B}</math>, then we can write the Rivlin neo-Heooken stress as | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J}\left[\bar{\boldsymbol{B}} - \tfrac{1}{3}\bar{I}_1\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}}\right] + 2D_1(J-1)\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J}\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}}) + 2D_1(J-1)\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
and the Ogden neo-Hookean stress as | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J}\left[\bar{\boldsymbol{B}} - \tfrac{1}{3}\bar{I}_1\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} -\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} \right] + 2D_1(J-1)\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J}\left[\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}})-\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}}\right] + 2D_1(J-1)\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
</math> | |||
The quantities | |||
:<math> | |||
p := -2D_1~J(J-1) ~;~~ p^{*} = -2D_1~J(J-1) + 2C_1 | |||
</math> | |||
have the form of [[pressure]]s and are usually treated as such. The Rivlin neo-Hookean stress can then be expressed in the form | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\tau} = J~\boldsymbol{\sigma} = -p\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2C_1~\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}}) | |||
</math> | |||
while the Ogden neo-Hookean stress has the form | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\tau} = -p^{*}\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2C_1~\mathrm{dev}(\bar{\boldsymbol{B}}) | |||
</math> | |||
|} | |||
=== Incompressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
For an '''incompressible''' neo-Hookean material with <math> J = 1</math> | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = -p~\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2C_1\boldsymbol{B} | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>p</math> is an undetermined pressure. | |||
== Cauchy stress in terms of principal stretches == | |||
=== Compressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
For a compressible neo-Hookean [[hyperelastic material]], the principal components of the Cauchy stress are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{i} = 2C_1 J^{-5/3} \left[ \lambda_i^2 -\cfrac{I_1}{3} \right] + 2D_1(J-1) ~;~~ i=1,2,3 | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, the differences between the principal stresses are | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}(\lambda_1^2-\lambda_3^2) ~;~~ | |||
\sigma_{22} - \sigma_{33} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}(\lambda_2^2-\lambda_3^2) | |||
</math> | |||
:{| class="toccolours collapsible collapsed" width="80%" style="text-align:left" | |||
!Proof: | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
For a compressible [[hyperelastic material]], the principal components of the Cauchy stress are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_i = \cfrac{\lambda_i}{\lambda_1\lambda_2\lambda_3}~\frac{\partial W}{\partial \lambda_i} ~;~~ i=1,2,3 | |||
</math> | |||
The strain energy density function for a compressible neo Hookean material is | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_1(\bar{I}_1-3) + D_1(J-1)^2 | |||
= C_1\left[J^{-2/3}(\lambda_1^2+\lambda_2^2+\lambda_3^2)-3\right] + D_1(J-1)^2 | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, | |||
:<math> | |||
\lambda_i\frac{\partial W}{\partial \lambda_i} = | |||
C_1\left[-\frac{2}{3}J^{-5/3}\lambda_i\frac{\partial J}{\partial \lambda_i}(\lambda_1^2+\lambda_2^2+\lambda_3^2) | |||
+2J^{-2/3}\lambda_i^2\right] + 2D_1(J-1)\lambda_i\frac{\partial J}{\partial \lambda_i} | |||
</math> | |||
Since <math>J = \lambda_1\lambda_2\lambda_3</math> we have | |||
:<math> | |||
\lambda_i\frac{\partial J}{\partial \lambda_i} = \lambda_1\lambda_2\lambda_3 = J | |||
</math> | |||
Hence, | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\lambda_i\frac{\partial W}{\partial \lambda_i} & = | |||
C_1\left[-\frac{2}{3}J^{-2/3}(\lambda_1^2+\lambda_2^2+\lambda_3^2) | |||
+2J^{-2/3}\lambda_i^2\right] + 2D_1J(J-1) \\ | |||
& = 2C_1J^{-2/3}\left[-\frac{1}{3}(\lambda_1^2+\lambda_2^2+\lambda_3^2) | |||
+\lambda_i^2\right] + 2D_1J(J-1) | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
The principal Cauchy stresses are therefore given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_i = 2C_1J^{-5/3}\left[ \lambda_i^2 -\cfrac{I_1}{3} \right] + 2D_1(J-1) | |||
</math> | |||
|} | |||
=== Incompressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
In terms of the [[finite strain theory|principal stretches]], the Cauchy stress differences for an '''incompressible''' hyperelastic material are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = \lambda_1~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_1} - \lambda_3~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_3}~;~~ | |||
\sigma_{22} - \sigma_{33} = \lambda_2~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_2} - \lambda_3~\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_3} | |||
</math> | |||
For an '''incompressible''' neo-Hookean material, | |||
:<math> | |||
W = C_1(\lambda_1^2 + \lambda_2 ^2 + \lambda_3 ^2 -3) ~;~~ \lambda_1\lambda_2\lambda_3 = 1 | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, | |||
:<math> | |||
\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_1} = 2C_1\lambda_1 ~;~~ | |||
\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_2} = 2C_1\lambda_2 ~;~~ | |||
\cfrac{\partial{W}}{\partial \lambda_3} = 2C_1\lambda_3 | |||
</math> | |||
which gives | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = 2(\lambda_1^2-\lambda_3^2)C_1 ~;~~ | |||
\sigma_{22} - \sigma_{33} = 2(\lambda_2^2-\lambda_3^2)C_1 | |||
</math> | |||
==Uniaxial extension== | |||
=== Compressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
[[Image:CompNeoHook.svg|thumb|350px|right|The true stress as a function of uniaxial stretch predicted by a compressible neo-Hookean material for various values of <math>C_1,D_1</math>. The material properties are representative of [[natural rubber]].]] | |||
For a compressible material undergoing uniaxial extension, the principal stretches are | |||
:<math> | |||
\lambda_1 = \lambda ~;~~ \lambda_2 = \lambda_3 = \sqrt{\tfrac{J}{\lambda}} ~;~~ | |||
I_1 = \lambda^2 + \tfrac{2J}{\lambda} | |||
</math> | |||
Hence, the true (Cauchy) stresses for a compressible neo-Hookean material are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\sigma_{11} & = \cfrac{4C_1}{3J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \tfrac{J}{\lambda}\right) + 2D_1(J-1) \\ | |||
\sigma_{22} & = \sigma_{33} = \cfrac{2C_1}{3J^{5/3}}\left(\tfrac{J}{\lambda} - \lambda^2\right) + 2D_1(J-1) | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
The stress differences are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \tfrac{J}{\lambda}\right) ~;~~ | |||
\sigma_{22} - \sigma_{33} = 0 | |||
</math> | |||
If the material is unconstrained we have <math>\sigma_{22} = \sigma_{33} = 0</math>. Then | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \tfrac{J}{\lambda}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
Equating the two expressions for <math>\sigma_{11}</math> gives a relation for <math>J</math> as a function of <math>\lambda</math>, i.e., | |||
:<math> | |||
\cfrac{4C_1}{3J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \tfrac{J}{\lambda}\right) + 2D_1(J-1) = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \tfrac{J}{\lambda}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
or | |||
:<math> | |||
D_1 J^{8/3} - D_1 J^{5/3} + \tfrac{C_1}{3\lambda} J - \tfrac{C_1\lambda^2}{3} = 0 | |||
</math> | |||
The above equation can be solved numerically using a [[Newton-Raphson]] iterative root finding procedure. | |||
=== Incompressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
[[Image:Moonie-Rivlin.PNG|thumb|350px|right|Comparison of experimental results (dots) and predictions for [[Hooke's law]](1), neo-Hookean solid(2) and [[Mooney-Rivlin solid]] models(3)]] | |||
Under uniaxial extension, <math>\lambda_1 = \lambda\,</math> and <math>\lambda_2 = \lambda_3 = 1/\sqrt{\lambda}</math>. Therefore, | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = 2C_1\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{1}{\lambda}\right) ~;~~ | |||
\sigma_{22} - \sigma_{33} = 0 | |||
</math> | |||
Assuming no traction on the sides, <math>\sigma_{22}=\sigma_{33}=0</math>, so we can write | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11}= 2C_1 \left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{1}{\lambda}\right) | |||
= 2C_1\left(\frac {3\varepsilon_{11} + 3\varepsilon_{11}^2 +\varepsilon_{11}^3} {1+\varepsilon_{11}}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
where <math> \varepsilon_{11}=\lambda-1 </math> is the engineering [[finite strain theory|strain]]. This equation is often written in alternative notation as | |||
:<math> | |||
T_{11}= 2C_1 \left(\alpha^2 - \cfrac{1}{\alpha}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
The equation above is for the '''true stress''' (ratio of the elongation force to deformed cross-section). For the [[engineering stress]] the equation is: | |||
:<math>\sigma_{11}^{\mathrm{eng}}= 2C_1 \left(\lambda - \cfrac{1}{\lambda^2}\right)</math> | |||
For small deformations <math>\varepsilon \ll 1</math> we will have: | |||
:<math>\sigma_{11}= 6C_1 \varepsilon = 3\mu\varepsilon</math> | |||
Thus, the equivalent [[Young's modulus]] of a neo-Hookean solid in uniaxial extension is <math>3\mu</math>, which is in concordance with linear elasticity (<math>E=2\mu(1+\nu)</math> with <math>\nu=0.5</math> for incompressibility). | |||
== Equibiaxial extension == | |||
=== Compressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
[[Image:CompNeoHookBiax.svg|thumb|350px|right|The true stress as a function of biaxial stretch predicted by a compressible neo-Hookean material for various values of <math>C_1,D_1</math>. The material properties are representative of [[natural rubber]].]] | |||
In the case of equibiaxial extension | |||
:<math> | |||
\lambda_1 = \lambda_2 = \lambda ~;~~ \lambda_3 = \tfrac{J}{\lambda^2} ~;~~ I_1 = 2\lambda^2 + \tfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4} | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\sigma_{11} & = 2C_1\left[\cfrac{\lambda^2}{J^{5/3}} - \cfrac{1}{3J}\left(2\lambda^2+\cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right)\right] + 2D_1(J-1) \\ | |||
& = \sigma_{22} \\ | |||
\sigma_{33} & = 2C_1\left[\cfrac{J^{1/3}}{\lambda^4} - \cfrac{1}{3J}\left(2\lambda^2+\cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right)\right] + 2D_1(J-1) | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
The stress differences are | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{22} = 0 ~;~~ \sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
If the material is in a state of plane stress then <math>\sigma_{33} = 0</math> and we have | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} = \sigma_{22} = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
We also have a relation between <math>J</math> and <math>\lambda</math>: | |||
:<math> | |||
2C_1\left[\cfrac{\lambda^2}{J^{5/3}} - \cfrac{1}{3J}\left(2\lambda^2+\cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right)\right] + 2D_1(J-1) = \cfrac{2C_1}{J^{5/3}}\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{J^2}{\lambda^4}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
or, | |||
:<math> | |||
\left(2D_1 - \cfrac{C_1}{\lambda^4}\right)J^2 + \cfrac{3C_1}{\lambda^4}J^{4/3} - 3D_1J - 2C_1\lambda^2 = 0 | |||
</math> | |||
This equation can be solved for <math>J</math> using Newton's method. | |||
=== Incompressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
For an incompressible material <math>J=1</math> and the differences between the principal Cauchy stresses take the form | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} - \sigma_{22} = 0 ~;~~ \sigma_{11} - \sigma_{33} = 2C_1\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{1}{\lambda^4}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
Under plane stress conditions we have | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_{11} = 2C_1\left(\lambda^2 - \cfrac{1}{\lambda^4}\right) | |||
</math> | |||
== Pure dilation == | |||
For the case of pure dilation | |||
:<math> | |||
\lambda_1 = \lambda_2 = \lambda_3 = \lambda ~:~~ J = \lambda^3 ~;~~ I_1 = 3\lambda^2 | |||
</math> | |||
Therefore, the principal Cauchy stresses for a compressible neo-Hookean material are given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\sigma_i = 2C_1\left(\cfrac{1}{\lambda^3} - \cfrac{1}{\lambda}\right) + 2D_1(\lambda^3-1) | |||
</math> | |||
If the material is incompressible then <math>\lambda^3 = 1</math> and the principal stresses can be arbitrary. | |||
The figures below show that extremely high stresses are needed to achieve large triaxial extensions or compressions. Equivalently, relatively small triaxial stretch states can cause very high stresses to develop in a rubber-like material. Note also that the magnitude of the stress is quite sensitive to the bulk modulus but not to the shear modulus. | |||
{| border="0" | |||
|- | |||
| valign="bottom"| | |||
[[Image:CompNeoHookTriax.svg|thumb|350px|right|The true stress as a function of equi-triaxial stretch predicted by a compressible neo-Hookean material for various values of <math>C_1,D_1</math>. The material properties are representative of [[natural rubber]].]] | |||
| valign="bottom"| | |||
[[Image:CompNeoHookTriaxJsvg.svg|thumb|350px|right|The true stress as a function of J predicted by a compressible neo-Hookean material for various values of <math>C_1,D_1</math>. The material properties are representative of [[natural rubber]].]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==Simple shear== | |||
For the case of [[simple shear]] the deformation gradient in terms of components with respect to a reference basis is of the form <ref name=Ogden>Ogden, R. W., 1984, '''Nonlinear elastic deformations''', Dover</ref> | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{F} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \gamma & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\gamma</math> is the shear deformation. Therefore the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor is | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{B} = \boldsymbol{F}\cdot\boldsymbol{F}^T = \begin{bmatrix} 1+\gamma^2 & \gamma & 0 \\ \gamma & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
=== Compressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
In this case <math>J = \det(\boldsymbol{F}) = 1</math>. Hence, <math> \boldsymbol{\sigma} = 2C_1\mathrm{dev}(\boldsymbol{B}) </math>. Now, | |||
:<math> | |||
\mathrm{dev}(\boldsymbol{B}) = \boldsymbol{B} - \tfrac{1}{3}\mathrm{tr}(\boldsymbol{B})\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} | |||
= \boldsymbol{B} - \tfrac{1}{3}(3+\gamma^2)\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} = | |||
\begin{bmatrix} \tfrac{2}{3}\gamma^2 & \gamma & 0 \\ \gamma & -\tfrac{1}{3}\gamma^2 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -\tfrac{1}{3}\gamma^2 \end{bmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
Hence the Cauchy stress is given by | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = | |||
\begin{bmatrix} \tfrac{4C_1}{3}\gamma^2 & 2C_1\gamma & 0 \\ 2C_1\gamma & -\tfrac{2C_1}{3}\gamma^2 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -\tfrac{2C_1}{3}\gamma^2 \end{bmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
=== Incompressible neo-Hookean material === | |||
Using the relation for the Cauchy stress for an incompressible neo-Hookean material we get | |||
:<math> | |||
\boldsymbol{\sigma} = -p\boldsymbol{\mathit{1}} + 2C_1\boldsymbol{B} = | |||
\begin{bmatrix} 2C_1(1+\gamma^2)-p & 2C_1\gamma & 0 \\ 2C_1\gamma & 2C_1 - p & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 2C_1 -p \end{bmatrix} | |||
</math> | |||
Thus neo-Hookean solid shows linear dependence of shear stresses upon shear deformation and quadratic dependence of the normal stress difference on the shear deformation. Note that the expressions for the Cauchy stress for a compressible and an incompressible neo-Hookean material in simple shear represent the same quantity and provide a means of determining the unknown pressure <math>p</math>. | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Hyperelastic material]] | |||
* [[Strain energy density function]] | |||
* [[Mooney-Rivlin solid]] | |||
* [[Finite strain theory]] | |||
* [[Stress measures]] | |||
[[Category:Continuum mechanics]] | |||
[[Category:Elasticity (physics)]] | |||
[[Category:Non-Newtonian fluids]] | |||
[[Category:Rubber properties]] | |||
[[Category:Solid mechanics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:20, 20 October 2013
Template:Continuum mechanics A neo-Hookean solid[1][2] is a hyperelastic material model, similar to Hooke's law, that can be used for predicting the nonlinear stress-strain behavior of materials undergoing large deformations. The model was proposed by Ronald Rivlin in 1948. In contrast to linear elastic materials, the stress-strain curve of a neo-Hookean material is not linear. Instead, the relationship between applied stress and strain is initially linear, but at a certain point the stress-strain curve will plateau. The neo-Hookean model does not account for the dissipative release of energy as heat while straining the material and perfect elasticity is assumed at all stages of deformation.
The neo-Hookean model is based on the statistical thermodynamics of cross-linked polymer chains and is usable for plastics and rubber-like substances. Cross-linked polymers will act in a neo-Hookean manner because initially the polymer chains can move relative to each other when a stress is applied. However, at a certain point the polymer chains will be stretched to the maximum point that the covalent cross links will allow, and this will cause a dramatic increase in the elastic modulus of the material. The neo-Hookean material model does not predict that increase in modulus at large strains and is typically accurate only for strains less than 20%.[3] The model is also inadequate for biaxial states of stress and has been superseded by the Mooney-Rivlin model.
The strain energy density function for an incompressible neo-Hookean material is
where is a material constant, and is the first invariant of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor, i.e.,
where are the principal stretches. For three-dimensional problems the compressible neo-Hookean material the strain energy density function is given by
where is a material constant, is the first invariant of the deviatoric part of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor, and is the deformation gradient. It can be shown that in 2D, the strain energy density function now becomes
Several alternative formulations exist for compressible neo-Hookean materials, for example [1]
For consistency with linear elasticity,
where is the shear modulus and is the bulk modulus.
Cauchy stress in terms of deformation tensors
Compressible neo-Hookean material
For a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material the Cauchy stress is given by
where is the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor, and
and the Cauchy stress can be expressed as
Comparison with Hooke's law shows that and .
Proof: The Cauchy stress in a compressible hyperelastic material is given by
For a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material,
while, for a compressible Ogden neo-Hookean material,
Therefore, the Cauchy stress in a compressible Rivlin neo-Hookean material is given by
while that for the corresponding Ogden material is
If the isochoric part of the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor is defined as , then we can write the Rivlin neo-Heooken stress as
and the Ogden neo-Hookean stress as
The quantities
have the form of pressures and are usually treated as such. The Rivlin neo-Hookean stress can then be expressed in the form
while the Ogden neo-Hookean stress has the form
Incompressible neo-Hookean material
For an incompressible neo-Hookean material with
where is an undetermined pressure.
Cauchy stress in terms of principal stretches
Compressible neo-Hookean material
For a compressible neo-Hookean hyperelastic material, the principal components of the Cauchy stress are given by
Therefore, the differences between the principal stresses are
Proof: For a compressible hyperelastic material, the principal components of the Cauchy stress are given by
The strain energy density function for a compressible neo Hookean material is
Therefore,
Hence,
The principal Cauchy stresses are therefore given by
Incompressible neo-Hookean material
In terms of the principal stretches, the Cauchy stress differences for an incompressible hyperelastic material are given by
For an incompressible neo-Hookean material,
Therefore,
which gives
Uniaxial extension
Compressible neo-Hookean material
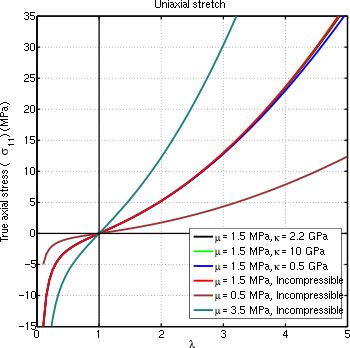
For a compressible material undergoing uniaxial extension, the principal stretches are
Hence, the true (Cauchy) stresses for a compressible neo-Hookean material are given by
The stress differences are given by
If the material is unconstrained we have . Then
Equating the two expressions for gives a relation for as a function of , i.e.,
or
The above equation can be solved numerically using a Newton-Raphson iterative root finding procedure.
Incompressible neo-Hookean material

Under uniaxial extension, and . Therefore,
Assuming no traction on the sides, , so we can write
where is the engineering strain. This equation is often written in alternative notation as
The equation above is for the true stress (ratio of the elongation force to deformed cross-section). For the engineering stress the equation is:
For small deformations we will have:
Thus, the equivalent Young's modulus of a neo-Hookean solid in uniaxial extension is , which is in concordance with linear elasticity ( with for incompressibility).
Equibiaxial extension
Compressible neo-Hookean material

In the case of equibiaxial extension
Therefore,
The stress differences are
If the material is in a state of plane stress then and we have
We also have a relation between and :
or,
This equation can be solved for using Newton's method.
Incompressible neo-Hookean material
For an incompressible material and the differences between the principal Cauchy stresses take the form
Under plane stress conditions we have
Pure dilation
For the case of pure dilation
Therefore, the principal Cauchy stresses for a compressible neo-Hookean material are given by
If the material is incompressible then and the principal stresses can be arbitrary.
The figures below show that extremely high stresses are needed to achieve large triaxial extensions or compressions. Equivalently, relatively small triaxial stretch states can cause very high stresses to develop in a rubber-like material. Note also that the magnitude of the stress is quite sensitive to the bulk modulus but not to the shear modulus.
 |
 |
Simple shear
For the case of simple shear the deformation gradient in terms of components with respect to a reference basis is of the form [1]
where is the shear deformation. Therefore the left Cauchy-Green deformation tensor is
Compressible neo-Hookean material
Hence the Cauchy stress is given by
Incompressible neo-Hookean material
Using the relation for the Cauchy stress for an incompressible neo-Hookean material we get
Thus neo-Hookean solid shows linear dependence of shear stresses upon shear deformation and quadratic dependence of the normal stress difference on the shear deformation. Note that the expressions for the Cauchy stress for a compressible and an incompressible neo-Hookean material in simple shear represent the same quantity and provide a means of determining the unknown pressure .
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Ogden, R. W. , 1998, Nonlinear Elastic Deformations, Dover. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Ogden" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ C. W. Macosko, 1994, Rheology: principles, measurement and applications, VCH Publishers, ISBN 1-56081-579-5.
- ↑ Gent, A. N., ed., 2001, Engineering with rubber, Carl Hanser Verlag, Munich.